As connected vehicles become central to the mobility ecosystem, automotive OEMs face a vital question: MQTT vs. HTTP — which protocol best supports vehicle telemetry? With global demand rising for real-time data exchange, secure diagnostics, and OTA updates, choosing the right communication protocol is no longer just a technical decision—it’s a strategic imperative. This article provides a deep dive into both protocols, comparing their suitability for scalable and reliable automotive connectivity.
Vehicle Telemetry in Connected Cars
Vehicle telemetry enables cars to send data—like location, diagnostics, and driving behavior—over networks to cloud platforms. This real-time data is crucial for applications such as:
- Predictive maintenance
- Over-the-air software updates
- Emergency call systems
- Driver behavior analysis
- Fleet tracking and optimization
MQTT and HTTP: A Technical Overview
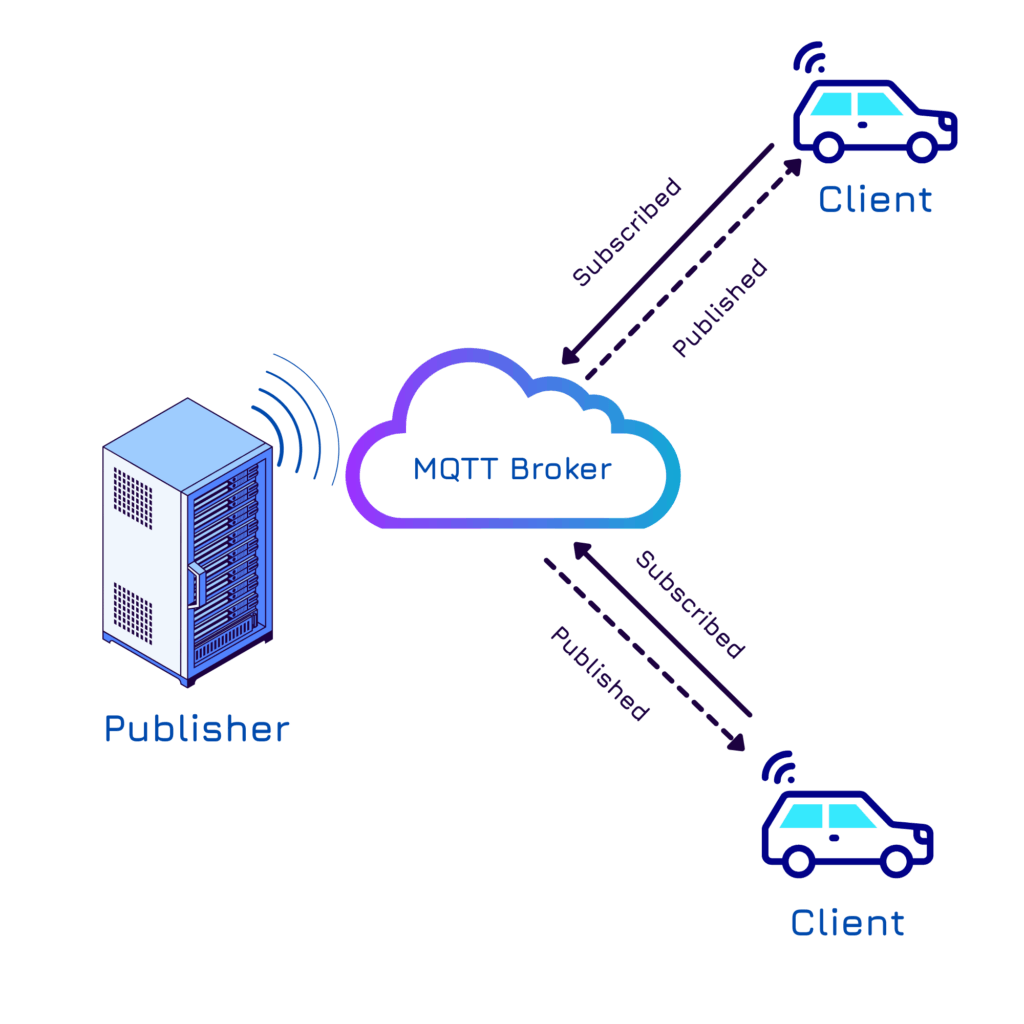
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport)
- Lightweight publish/subscribe model
- Optimized for low bandwidth and high-latency environments
- Supports Quality of Service (QoS) levels for message reliability
- Efficient battery and data usage
- Ideal for real-time, continuous data streaming
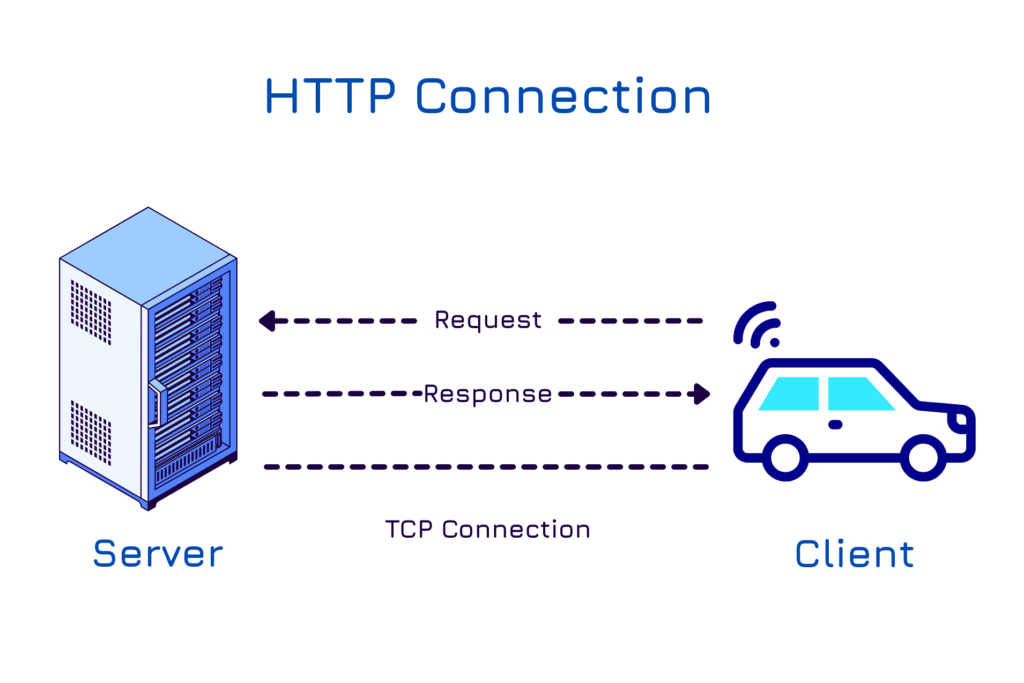
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
- Traditional request/response model
- Stateless and widely supported across platforms
- Well-suited for large, infrequent data transfers
- Heavier on bandwidth and latency
- Used for event-based updates or cloud API calls
MQTT vs. HTTP: Which Fits Vehicle Telemetry Better?
| Feature | MQTT | HTTP |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Model | Bi-directional (Pub/Sub) | One-way (Request/Response) |
| Data Efficiency | Highly efficient | Less efficient |
| Power Consumption | Low | Higher |
| Latency | Very low | Higher |
| Network Resilience | Better in unstable networks | Requires stable connection |
| Ideal Use Cases | Real-time telemetry, alerts | OTA updates, API queries |
Use Case Examples: When to Use Each Protocol
Use MQTT for:
- Real-time location updates
- Live engine diagnostics
- Emergency alerts (e.g., eCall)
- Fleet data synchronization
Use HTTP for:
- Firmware and OTA updates
- Regulatory data uploads
- Periodic diagnostics
- Cloud server interactions
Global Adoption Trends
The shift toward electric and autonomous vehicles has accelerated the adoption of MQTT for real-time communication. According to IoT Analytics (2023), MQTT usage in automotive applications has increased by over 75% globally, driven by demand for low-latency, high-efficiency communication in EV platforms and connected fleets. Regions like the EU and China lead this transformation, adopting MQTT-based architectures for advanced telematics and V2X systems.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Protocol
Deciding between MQTT vs. HTTP for vehicle telemetry depends on an OEM’s specific connectivity goals. MQTT excels in real-time, low-power, always-on applications, making it a top choice for most modern connected vehicle systems. HTTP, on the other hand, still holds value in scenarios requiring robust API interaction or infrequent data transmissions.
At the end of the day, Horizon Connect helps automotive OEMs align their protocol architecture with the demands of smart, connected mobility—globally and reliably.